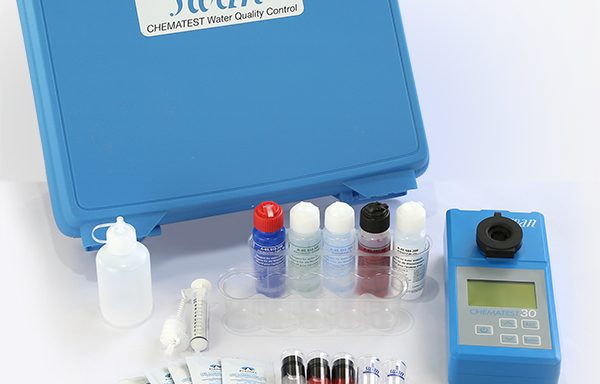
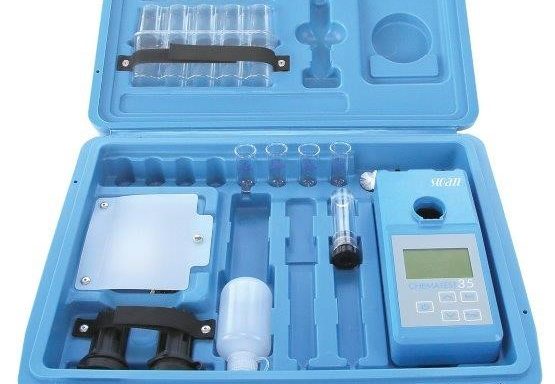
What is Chlorine?
Chlorine (Cl) is a chemical element with the atomic number 17, situated in group 17 of the periodic table, known as the halogens. It is distinguished by its greenish-yellow colour and pungent odour. At room temperature, chlorine exists as a diatomic gas (Cl2), making it highly reactive and capable of combining with nearly all other elements. Due to its reactivity, chlorine is not found free in nature but is commonly present in compounds like sodium chloride (table salt). A chlorine analyser is often used to monitor and control chlorine levels in various applications. Chlorine plays an essential role in water purification, disinfection, and the production of a wide range of organic and inorganic chemicals.
Monitoring Chlorine in Water
Monitoring chlorine levels in water supplies is crucial for ensuring public health and safety. Chlorine, commonly used as a disinfectant, is vital in water treatment for eliminating harmful pathogens that can cause waterborne diseases. To maintain optimal water quality, it is essential to measure and record chlorine residuals regularly.
Public water systems, particularly those serving large populations or using surface water sources, are often required to conduct continuous monitoring of residual chlorine to comply with regulatory standards. This practice helps adjust dosages for effective disinfection and prevents the formation of potentially harmful disinfection by-products. The significance of accurate chlorine monitoring is highlighted by its direct impact on the distribution system’s optimisation program, where chlorine residual levels serve as key indicators of water quality integrity. As technology advances, new and improved methods for monitoring chlorine in water are being developed, enhancing the ability to protect drinking water from contamination and ensure its safety for public consumption.
Chlorine Analyser Parameters and Applications
- Bound Chlorine Analysers
- Chlorine Dioxide Analysers
- Disinfectant Analysers
- Free Chlorine Analysers
- Total Chlorine Analysers
- Renal Dialysis Total Chlorine Monitor
Online Chlorine Analysers